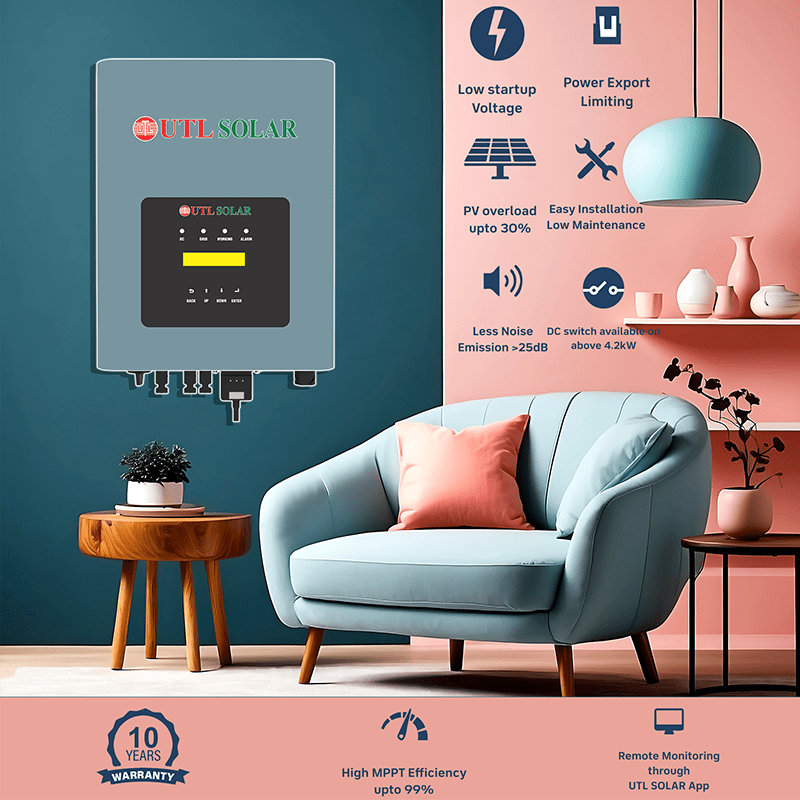
Solar inverter is a sophisticated device that converts direct current(DC) from the solar panels into alternating current(AC). This AC current can be used to power multiple appliances in your home, office, or any other commercial establishments.
How does a solar inverter work?
A solar inverter is a device that helps you use electricity from the sun to power your home. Here’s a simple step-by-step explanation of how it works.
Solar Panels Capture Sunlight
- Solar panels are placed on the roof of your house.
- These panels capture sunlight and turn it into Direct Current (DC).
DC Electricity Needs Conversion
- The electricity from the solar panels is in DC form.
- Most of the appliances in your home use Alternating Current (AC).
- This means the DC current needs to be converted into AC current.
The Role of the Solar Inverter:
- The solar inverter is connected to the solar panels.
- It converts the DC current from the panels into AC current.
- Now, the electricity is ready to be used by your home appliances.
Using Solar Energy in Your Home:
- The converted AC current flows from the inverter to your home’s electrical system.
- You can now use this solar energy to power your lights, fans, TV, and other appliances.
Extra Energy Goes to the Grid:
- Sometimes, the solar panels produce more electricity than your home needs.
- This extra electricity is sent back to the power grid.
- Your electricity company might give you credit or pay you for this extra energy.
What Happens at Night:
- At night or on cloudy days, the solar panels don’t produce electricity.
- If you have a grid-tied system, your home will use electricity from the grid.
- If you have batteries, they store extra energy from the day to use at night.
Solar Inverter Technologies
PWM (Pulse Width Modulation)
PWM is a basic technology used in some solar charge controllers and inverters. It regulates the charging of batteries by controlling the width of pulses sent to the battery bank from the solar panels. PWM inverters operate at a fixed voltage and are simpler in design compared to MPPT inverters. However, they are less efficient, especially when solar panel conditions vary.
MPPT (Maximum Power Point Tracking)
MPPT is an advanced technology used in many modern solar inverters. It maximizes the energy output from solar panels by continuously adjusting the voltage and current to operate at the panel’s maximum power point. This allows MPPT inverters to efficiently convert the variable DC output from solar panels into AC electricity, optimizing energy harvest even under changing weather conditions or shading.
r-MPPT (Rapid Maximum Power Point Tracking)
r-MPPT, or Rapid Maximum Power Point Tracking, is an advanced variant of MPPT technology used in some high-performance solar inverters. This is a patented technology by UTL Solar. It enhances the system’s efficiency by rapidly and accurately tracking the maximum power point (MPP) of solar panels. This allows the inverter to adjust quickly to changes in sunlight intensity and panel conditions, optimizing energy conversion efficiency.
Difference Between Solar Inverter and Normal Inverter
Feature | Solar Inverter | Normal Inverter |
Primary Function | Converts DC from solar panels to AC for home use | Converts DC from batteries to AC for home use |
Energy Source | Solar panels and batteries | Only batteries (charged from the grid) |
Grid Interaction | Can be grid-connected or off-grid | Typically off-grid |
Battery Charging | Charges batteries using solar energy | Charges batteries using grid electricity |
Efficiency | High efficiency due to optimized solar energy usage | Moderate efficiency, dependent on grid electricity |
Cost | Higher initial investment | Lower initial cost |
Environmental Impact | Environmentally friendly, reduces carbon footprint | Higher carbon footprint due to reliance on grid power |
Backup Power | Provides backup during power outages | Provides backup during power outages |
Subsidy and Incentives | Often eligible for government subsidies and incentives | Generally not eligible for subsidies |
Maintenance | Requires minimal maintenance for solar panels | Requires battery maintenance |
Net Metering | Can export excess energy to the grid (net metering) | Does not have net metering capabilities |
Lifespan | Typically longer due to solar component durability | Depends on battery life |
Application | Ideal for homes looking to reduce electricity bills and use renewable energy | Ideal for homes needing backup power during outages |
Factors to Consider Before Buying Solar Inverters
Buying solar inverters is a big decision, and you need every important detail to come to a decision. Let’s make it a bit easier:
- Calculate Your Energy Consumption and Power Source: Determine your household or business energy requirements to choose an inverter that can handle your power needs efficiently.
- Decide on the Type of Inverter: On-Grid, Off-Grid, or Hybrid
On-Grid Inverters: Connected to the grid, these are suitable if you have regular grid power and want to save electricity bills.
Off-Grid Inverters: Ideal for remote locations with no grid access, these require batteries to store excess energy.
Hybrid Inverters: Combine features of both on-grid and off-grid inverters, offering flexibility and backup power solutions. - Choose the Right Brand
Avoid selecting a brand solely based on popularity. Investigate the company’s reputation for customer service, as it can vary significantly.
Look for real customer reviews on platforms like YouTube, as Google reviews can sometimes be fabricated. - Consider Long-Term Costs, Not Just Upfront Prices
Some brands may offer inverters at a lower initial cost, but they might end up being more expensive in the long run due to maintenance, efficiency, and reliability issues. - Check the Warranty Structure and Coverage Policies
Ensure the inverter comes with a comprehensive warranty that covers parts and labor. Understand the duration and terms of the warranty to avoid future surprises. - Always Go for the Latest Technology in the Market
Technological advancements in solar inverters can lead to higher efficiency and better performance. Investing in the latest technology ensures you get the most out of your solar power system.